News
Site Editor
 Site
/uploads/image/667d0e0257f45.png
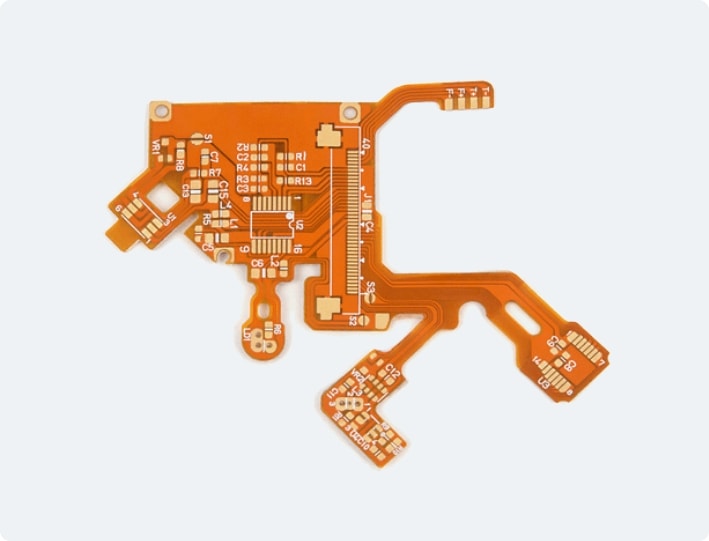
Flexible PCBs are a type of printed circuit board that is characterized by its ability to bend, twist, and flex without breaking or damaging the conductive traces. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs that are made of rigid materials like fiberglass or epoxy, flexible PCBs are made of flexible plastic materials such as polyimide (PI) or polyester (PET). These materials offer excellent flexibility, durability, and thermal resistance, making them suitable for applications that require a high degree of flexibility.
Site
/uploads/image/667d0e0257f45.png
Flexible PCBs are a type of printed circuit board that is characterized by its ability to bend, twist, and flex without breaking or damaging the conductive traces. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs that are made of rigid materials like fiberglass or epoxy, flexible PCBs are made of flexible plastic materials such as polyimide (PI) or polyester (PET). These materials offer excellent flexibility, durability, and thermal resistance, making them suitable for applications that require a high degree of flexibility.
What is flexible pcb
Views: 1639
Author: Site Editor
Publish Time: 2023-07-18
Origin: Site
Flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs) have revolutionized the electronics industry by enabling the creation of lightweight, flexible, and compact electronic devices. Also known as flex circuits, they are widely used in various applications, including consumer electronics, medical devices, automotive systems, and aerospace technology. In this article, we will explore what flexible PCBs are and delve into their advantages, construction, and applications.
What are Flexible PCBs
Flexible PCBs are a type of printed circuit board that is characterized by its ability to bend, twist, and flex without breaking or damaging the conductive traces. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs that are made of rigid materials like fiberglass or epoxy, flexible PCBs are made of flexible plastic materials such as polyimide (PI) or polyester (PET). These materials offer excellent flexibility, durability, and thermal resistance, making them suitable for applications that require a high degree of flexibility.
Construction of Flexible PCBs
Flexible PCBs are composed of multiple layers of flexible materials laminated together with adhesive layers. The base layer is usually made of a flexible plastic substrate, such as polyimide film, which provides the board with its inherent flexibility. On top of the base layer, a layer of copper is laminated to create the conductive traces. These traces are etched using a chemical process to achieve the desired circuit pattern.
To protect the conductive traces from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and temperature variations, a layer of solder mask is applied. This solder mask is a thin coating that covers the conductive traces, leaving only the intended contact points exposed. Additionally, a layer of protective coverlay or encapsulant is added to provide further strength and protection to the board.
Advantages of Flexible PCBs
Flexible PCBs offer several advantages over rigid PCBs, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Firstly, their flexibility allows for easier integration and installation in space-constrained devices or irregularly shaped products. Their lightweight nature also helps reduce the overall weight of the device. Additionally, flexible PCBs can tolerate higher levels of vibration and shock, making them ideal for applications where durability is crucial.
Moreover, the use of flexible PCBs can simplify the circuit design and reduce the number of interconnections, as they can be folded or bent to fit into tight spaces. This overall reduction in interconnects improves the reliability and signal integrity of the device. Furthermore, flexible PCBs offer better resistance to thermal cycling, ensuring stable performance even in harsh operating conditions.
Applications of Flexible PCBs
The versatility and unique characteristics of flexible PCBs make them suitable for a wide range of applications. They are commonly used in consumer electronics such as smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices, where their flexibility allows for sleeker and more ergonomic designs. In the medical field, flexible PCBs find applications in medical implants, diagnostic equipment, and body-worn monitoring devices, thanks to their biocompatibility and flexibility.
Furthermore,
flexible PCBs are extensively used in the automotive industry for various applications like smart lighting systems, engine control units, and infotainment systems. Their ability to withstand vibrations, shocks, and temperature fluctuations makes them ideal for automotive environments. Additionally, flexible PCBs are playing a crucial role in aerospace technology, enabling the construction of lightweight and reliable systems for satellites, spacecraft, and avionics.
Conclusion
Flexible PCBs have revolutionized the electronics industry with their flexibility, durability, and lightweight characteristics. Their unique construction and advantages make them an ideal choice for a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics and medical devices to automotive systems and aerospace technology. As technology continues to advance, flexible PCBs are expected to play an increasingly important role in enabling the development of innovative and efficient electronic devices.