Technology
Stiffener
Three common types of Stiffener in PCB:Steel Stiffener,FR4 Stiffener and PI Stiffener
In the PCB industry, stiffener refers to the measures taken during the design, manufacturing, or assembly processes to enhance the structural strength, rigidity, and stability of the circuit board. Due to factors such as mechanical stress, vibration, and temperature variations, PCBs may experience challenges that could affect their performance. stiffener techniques aim to improve the durability and reliability of the PCB, ensuring its proper functioning in various application environments.Let's first introduce the meaning and characteristics of these three types of stiffener in PCB: Steel Stiffener,FR4 Stiffener and PI Stiffener.
Steel Stiffener
Steel stiffener is a technique used to enhance the structural strength and stability of printed circuit boards by adding metal steel plates to specific areas. These steel plates are typically made of stainless steel or other high-strength metal materials and can be securely attached to the PCB using screws, welding, or other fixation methods. Steel stiffener is primarily used in applications that require additional support and rigidity, such as mechanical devices or PCBs operating in high-vibration environments.
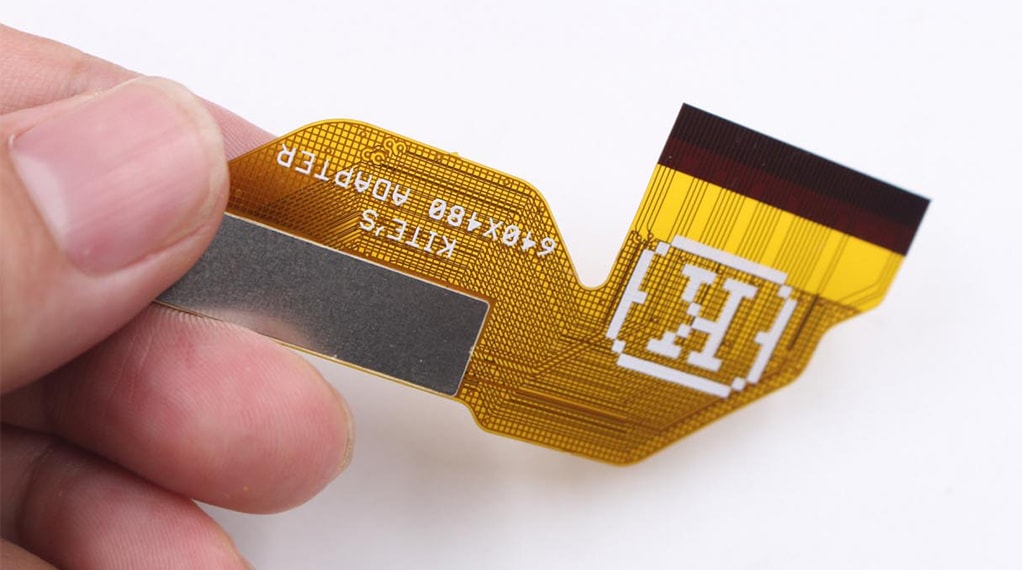
FR4 Stiffener
FR4 stiffener involves strengthening the PCB by using thicker FR4 substrates or increasing the number of FR4 layers in the design. FR4 is a commonly used glass fiber-reinforced epoxy resin substrate that offers good mechanical properties and thermal stability. Increasing the thickness or layer count of FR4 enhances the rigidity and flexural strength of the PCB, making it suitable for applications that demand higher mechanical strength.
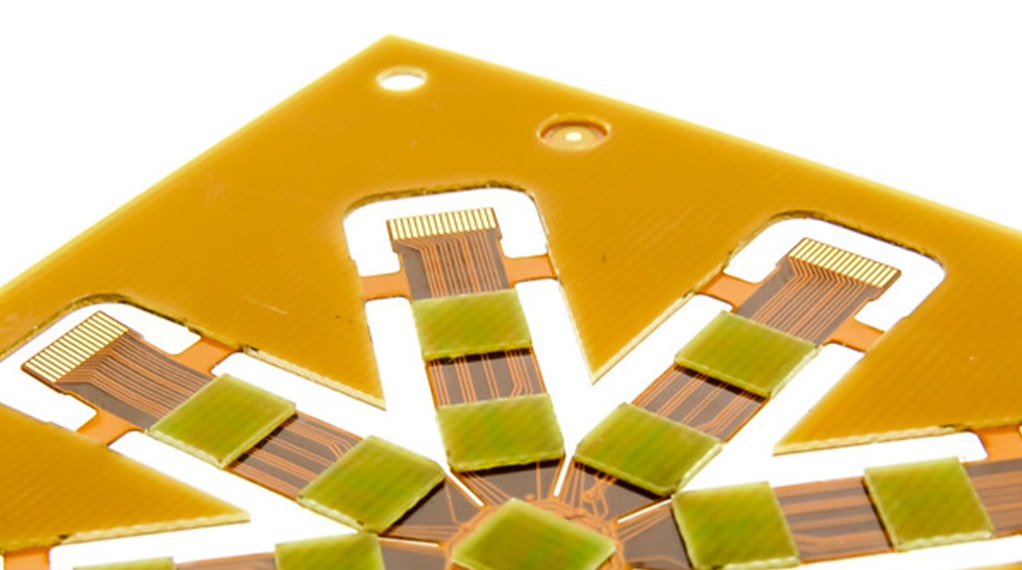

PI Stiffener
PI stiffener entails using polyimide (PI) materials to enhance the strength and stability of PCBs during the manufacturing process. PI is a high-performance polymer with excellent heat resistance, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation properties. PI stiffener is typically achieved by adding additional PI layers or using PI composite materials in specific areas of the PCB, providing additional rigidity and impact resistance. It is well-suited for high-temperature and high-reliability applications, such as aerospace and automotive electronics.
These stiffener methods are selected based on specific application requirements and environmental conditions in PCB manufacturing. They offer additional strength, rigidity, and stability, ensuring that PCBs perform exceptionally well and remain reliable under various operating conditions.


